It’s likely that earwax and its buildup haven’t been subjects of significant contemplation for you, except maybe during ear hygiene sessions. Still, it’s essential to have an understanding of its purpose and how it forms.
What causes the accumulation of earwax?
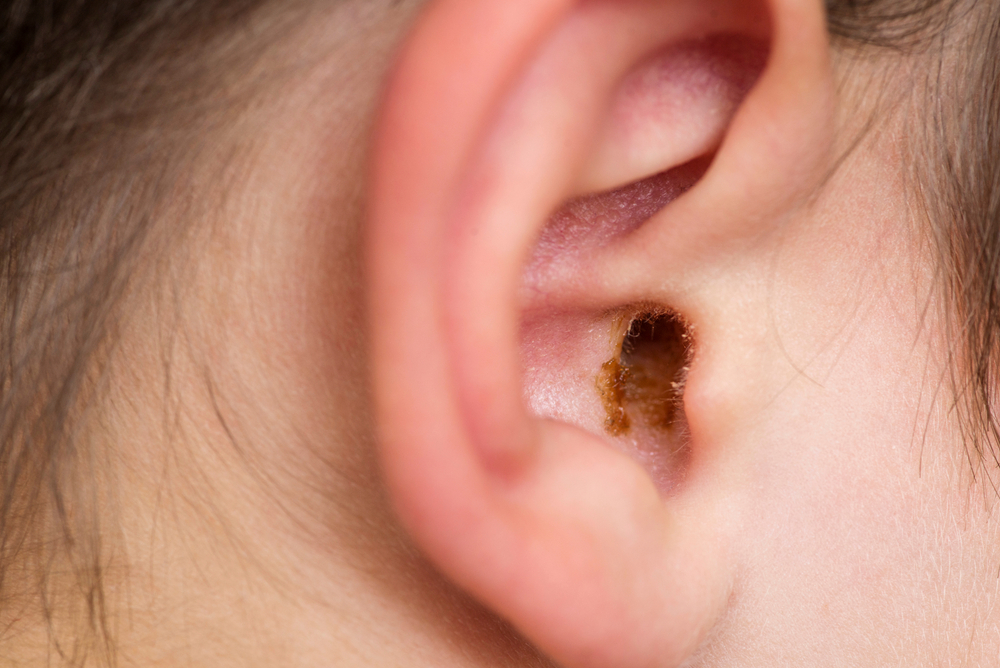
Earwax, also scientifically called cerumen, is composed of a mix of sweat, skin particles, hair, debris, and ceruminous gland secretions. This earwax presents with a waxy texture and can show shades of orange, yellow, gray, or brown.
In most circumstances, children tend to produce more earwax than adults. Children also typically have softer earwax that’s lighter in color than adults.
Earwax passes the outer ear canal leisurely, eventually reaching the ear opening, where it either self-expels or gets washed away when you bathe.
Why do we need earwax?
Earwax serves several essential functions, such as:
- Before things such as dust, dirt, or other external debris go further up into the ear canal, earwax acts as a roadblock.
- Helping prevent ear infections.
- Protecting and lubricating the skin lining the ear canal, thus preventing dryness and itchiness.
Blockages caused by earwax
Typically, there’s no imperative need to remove earwax from your ears unless it becomes impacted, a common issue associated with earwax. Impacted earwax can stem from narrow or unusually shaped ear canals impeding the natural movement of earwax toward the ear’s opening.
Wax can be unintentionally pushed up into the ear canal by utilizing poor cleaning practices like using cotton swabs.
People wrestling with hearing loss who make use of earplugs or hearing aids are also predisposed to experiencing ear canal obstructions.
How excessive earwax can affect hearing
Auditory health might be hindered and you might feel minor discomfort.
Additionally, considerable accumulations of earwax can induce tinnitus, a feeling of ringing in the ears.
Acoustic trauma might lead to long-term hearing impairment, perforated eardrums, and long-term hearing loss if earwax blockages go ignored.
Addressing impacted earwax
If you think you have an earwax blockage, consulting us quickly is imperative. You may be advised to use over-the-counter products like a bulb syringe or earwax softening drops to clear the wax out, depending on the severity of the blockage.
If you’re worried about your earwax buildup, call us right away to schedule an appointment.